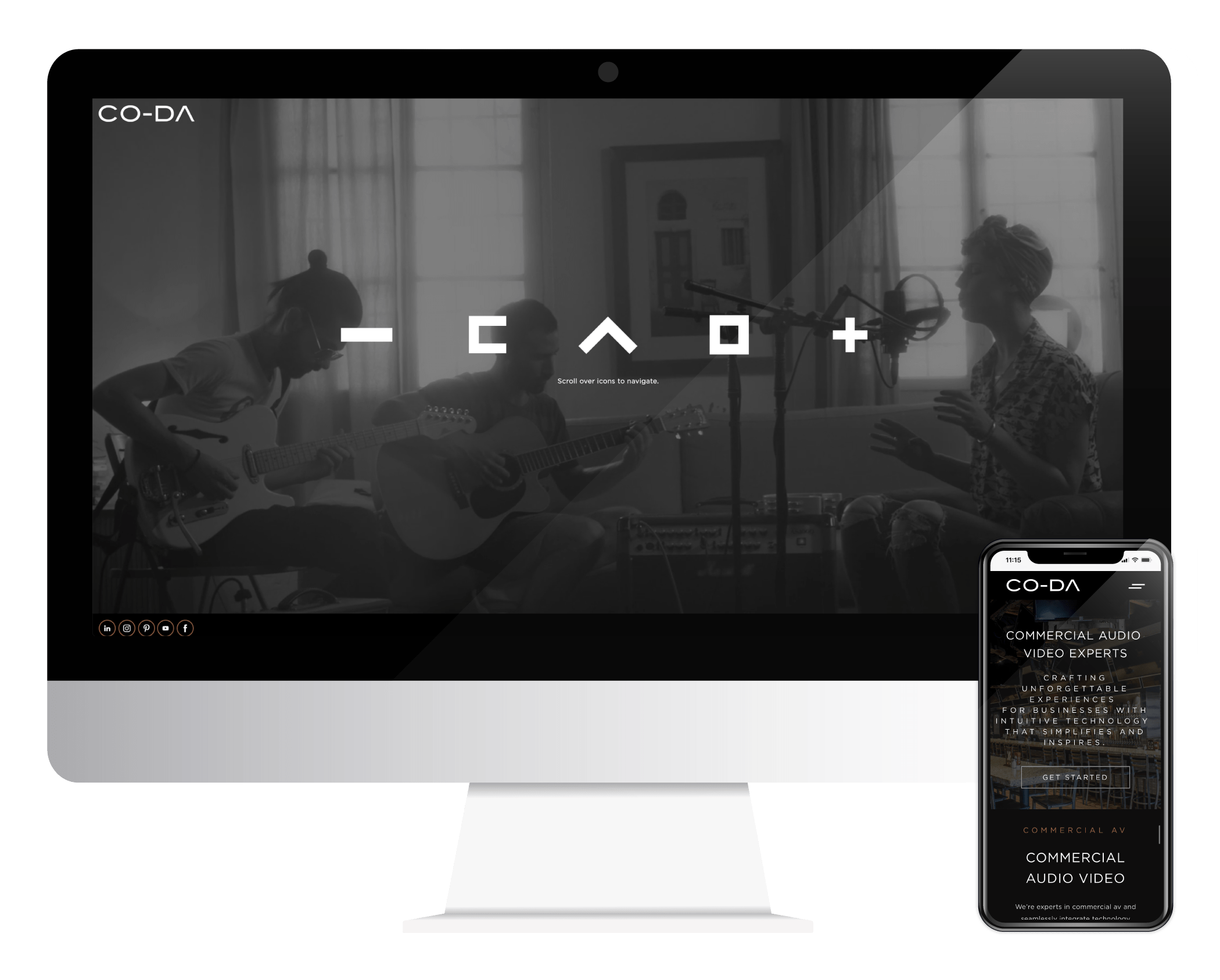
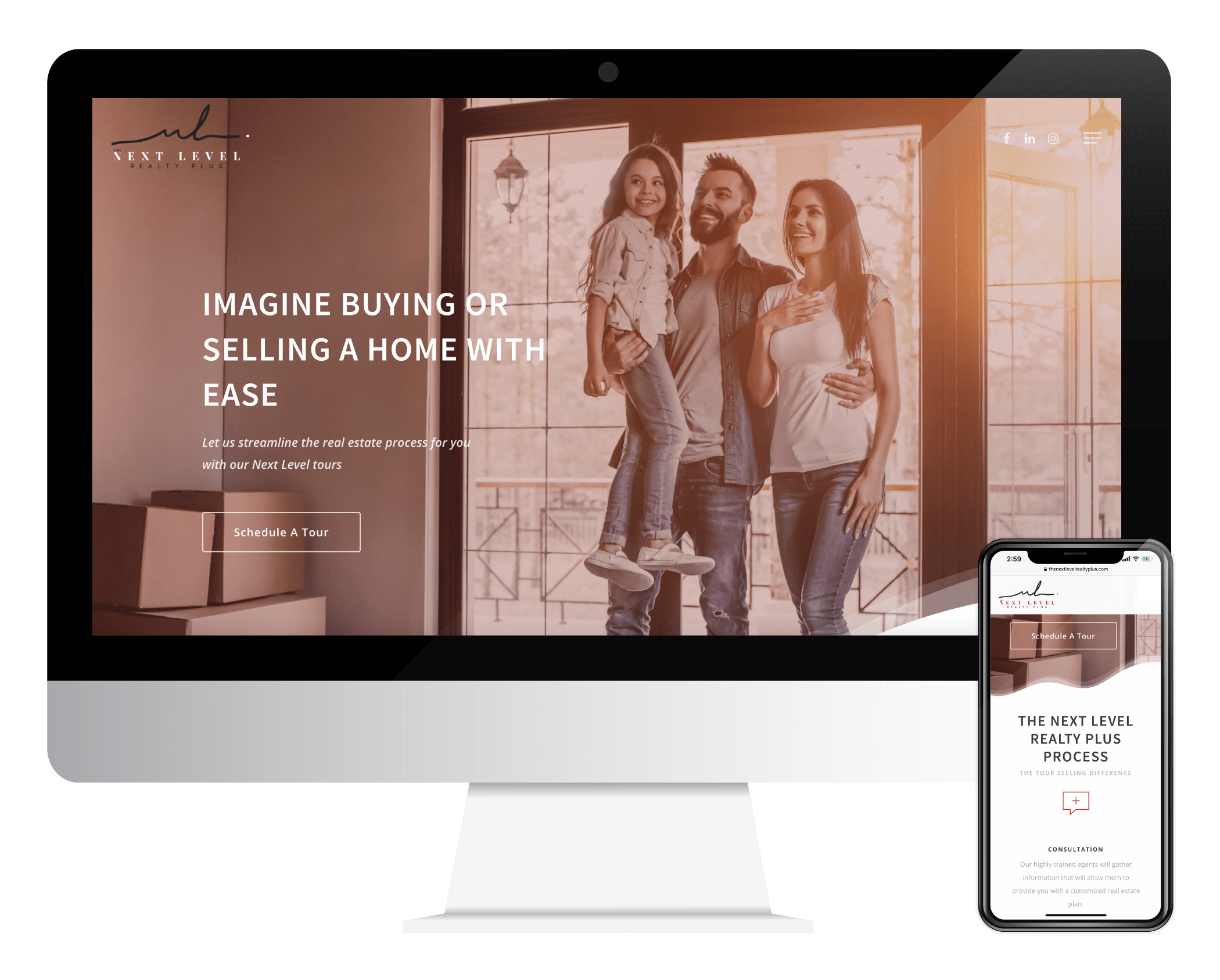
Design-driven marketing agency that teams up with extraordinary companies to achieve big things.
Captivate Your Audience
Grow Your Business
Do What You Love
Design the Website of Your Dreams

State of the Art Design
We employ modern design techniques to create stunning and effective websites.
Simple and Clear Navigation
Your website is your story to the world so we make sure to tell it clearly.
Responsive
All of our designs are developed to display clearly on all browsers and devices.
Mobile First Approach
Over 5 billion smart phone users and 53% search traffic on mobile makes it critical to have a mobile first design.
Your In-House Marketing Team
A design-driven marketing agency that teams up with extraordinary companies to achieve big things.
Website Design
Build a beautiful website that you’re proud to show to the world.
Digital Marketing
Design a digital marketing machine that drives qualified leads to grow your business.
Conversion Optimization
Use data to optimize landing pages and ads to make sure you’re converting customers.